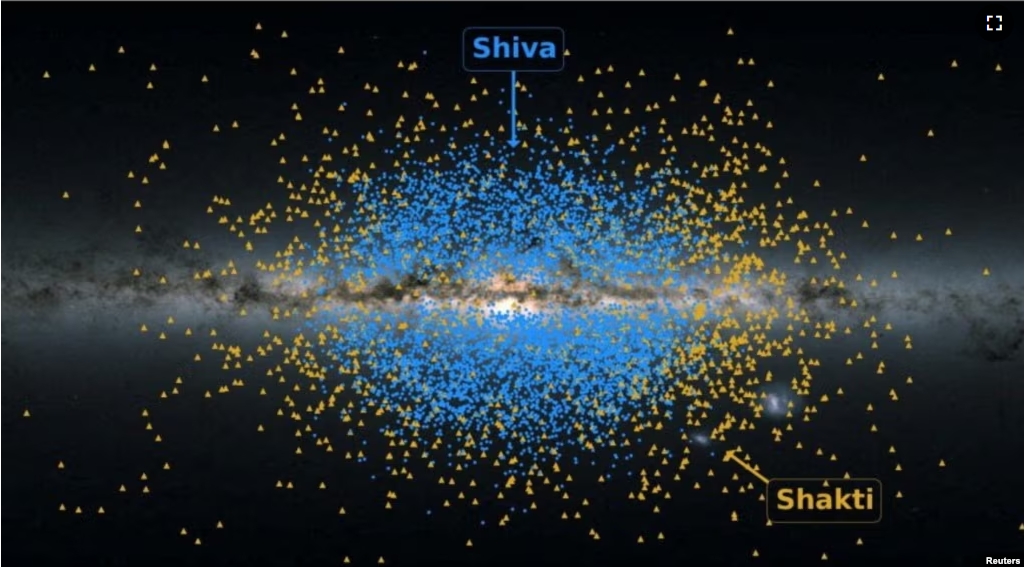
Researchers have identified two ancient star groupings that appear to be among the Milky Way Galaxy’s earliest parts.
The structures are named after the Hindu gods Shakti and Shiva. They were discovered using observations from the European Space Agency’s Gaia space telescope.
Scientists wrote in a study that the structures might be the remains of two galaxies that combined 12 billion years ago with the early pieces of the Milky Way. They said the discovery offers new information about how our galaxy formed.
Researchers said Shakti and Shiva are made up of stars that contain similar chemicals. They are believed to have formed 12 to 13 billion years ago. Each of the structures has a mass 10 million times greater than our sun.
Astronomer Khyati Malhan of the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Germany was the lead writer of the study. It was recently published in The Astrophysical Journal. Malhan said the study deals with a central question: “how do galaxies form in our universe?”
The Milky Way is a large spiral-shaped galaxy made up of hundreds of billions of stars. It is a large, flat circle about 100,000 light years across. A light year is the distance light travels in a year.
Malhan said the study might have identified the last event before the Milky Way began to take the shape it has today.
The European Space Agency launched Gaia in 2013. The space telescope is helping to create the largest and most complete three-dimensional map of the Milky Way. The telescope is measuring the positions, distances, and movements of the stars. This data permitted researchers to find Shakti and Shiva.
The researchers said Shiva and Shakti are now within 30,000 light years of the galaxy’s center.

The study builds on another recent discovery. In 2022, scientists using Gaia data identified what they called the “poor old heart” of the Milky Way. It is made up of a population of stars from the earliest period of the galaxy found near its center.
The stars that make up Shiva and Shakti are different chemically from most of the Milky Way’s other stars. They are called “metal poor” because of the amount of heavy elements they contain. For example, the stars have less iron, carbon, and oxygen than similar stars in other parts of the galaxy
Heavier elements first formed inside the universe’s earliest population of stars. When these stars exploded at the end of their life cycles, the elements were then sent out into space.
Malhan said researchers would like to “trace the formation and evolution of the Milky Way starting from the beginning of it until present day.” But he said this is difficult because the earliest period of the galaxy took place 11 to 12 billion years ago.
Scientists say the Big Bang event started the formation of the universe about 13.8 billion years ago.
I’m Gregory Stachel.
Will Dunham reported this story for Reuters. Gregory Stachel adapted it for VOA Learning English.
__________________________________________________
Words in This Story
galaxy – n. any one of the very large groups of stars that make up the universe
spiral – n. a circular curving line that goes around a central point while getting closer to or farther away from it
three-dimensional – adj. having or seeming to have length, width, and depth
cycle – n. a set of events or actions that happen again and again in the same order
trace – v. to follow (something) back to its cause, beginning, or origin: to find out where something came from
evolution – n. a process of slow change and development