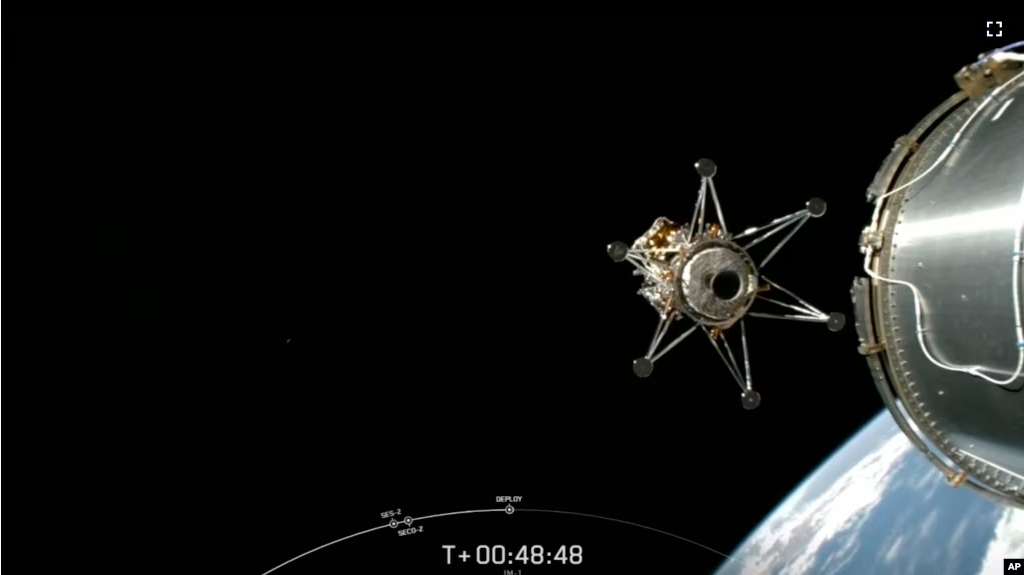
The U.S. space agency NASA has launched a moon lander built by a private U.S. company aiming to reach the moon next week. Thursday’s launch came after a failed attempt from another private American company last month.
SpaceX’s Falcon rocket launched Intuitive Machines’ lunar lander to the moon, 370,000 kilometers away, from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
The American space agency is the main sponsor for the private mission with six navigation and other technology experiments on the lander. If all goes well, the lunar spacecraft will try to land on February 22, after one day in lunar orbit.
Five countries — the U.S., Russia, China, India and Japan — have landed a spacecraft on the moon. No private company has yet to succeed in doing so. Only the U.S. has sent astronauts to the moon. Apollo 17’s Gene Cernan and Harrison Schmitt were the last of the Apollo program’s astronauts to reach the moon in December 1972.
“There have been a lot of sleepless nights getting ready for this,” Intuitive Machines’ co-founder and chief executive Steve Altemus said before the flight.
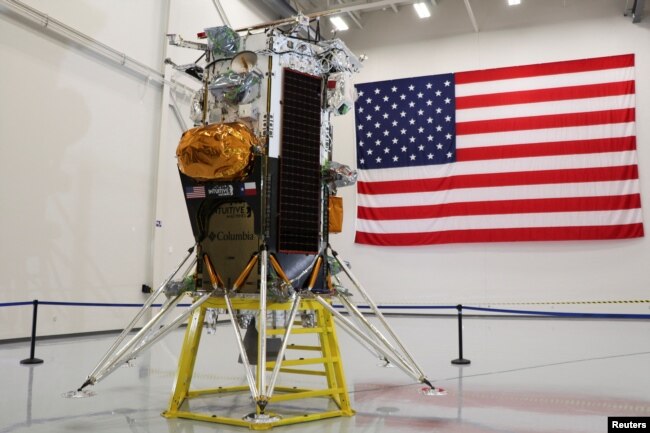

The Houston-based company aims to land its 4.3-meter tall, six-legged spacecraft near the moon’s south pole. The area is full of dangerous craters and cliffs but it is possibly rich in frozen water. It is also the place where NASA plans to land astronauts in a few years.
Last month, Peregrine, a lunar lander from privately-owned Astrobotic Technology, failed shortly after liftoff. The spacecraft, which carried some NASA experiments, broke apart and burned up 10 days after launch partly because of a fuel leak.
Other attempts made it to the moon before wrecking.
An Israeli nonprofit group’s lander crashed in 2019. Last year, a Japanese company saw its lander crash into the moon followed by Russia’s crash landing.
Intuitive Machines named its lander after Homer’s hero in The Odyssey.
“Godspeed, Odysseus. Now let’s go make history,” said Trent Martin of Intuitive Machines.
NASA is paying Intuitive Machines $118 million to get its latest set of experiments to the moon. The company also gets payment from businesses. They include Columbia Sportswear, which is testing material as a thermal insulator on the lander, and artist Jeff Koons, who is sending his small moon figurines to Earth’s natural satellite.
The lander is also carrying Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University’s Eaglecam. The camera is designed to take pictures of the lander as it lands.
The spacecraft will cease operations after a week on the moon’s surface.
I’m Dan Friedell.
Marcia Dunn reported this story for the Associated Press. Hai Do adapted it for VOA Learning English.
_________________________________________________
Words in This Story
sponsor –n. a person or group that supports either a person or activity with money and effort
navigation –n. related to the science of getting vehicles from one place to another
crater –n. the mark left on the surface of a planet, moon or asteroid after it is hit by a space object
cliff –n. a surface that is very steep dropping from a high to a lower place
thermal insulator –n. a material that protects equipment from heat
figurine –n. a little statue